BANKSY unifies cell typing and tissue domain segmentation for scalable spatial omics data analysis
Published in Nature Genetics, 2024
BANKSY is an algorithm with R and Python implementations that identifies both cell types and tissue domains from spatially-resolved -omics data by incorporating spatial kernels capturing microenvironmental information, applicable to a range of spatially-resolved technologies, and scalable to millions of cells.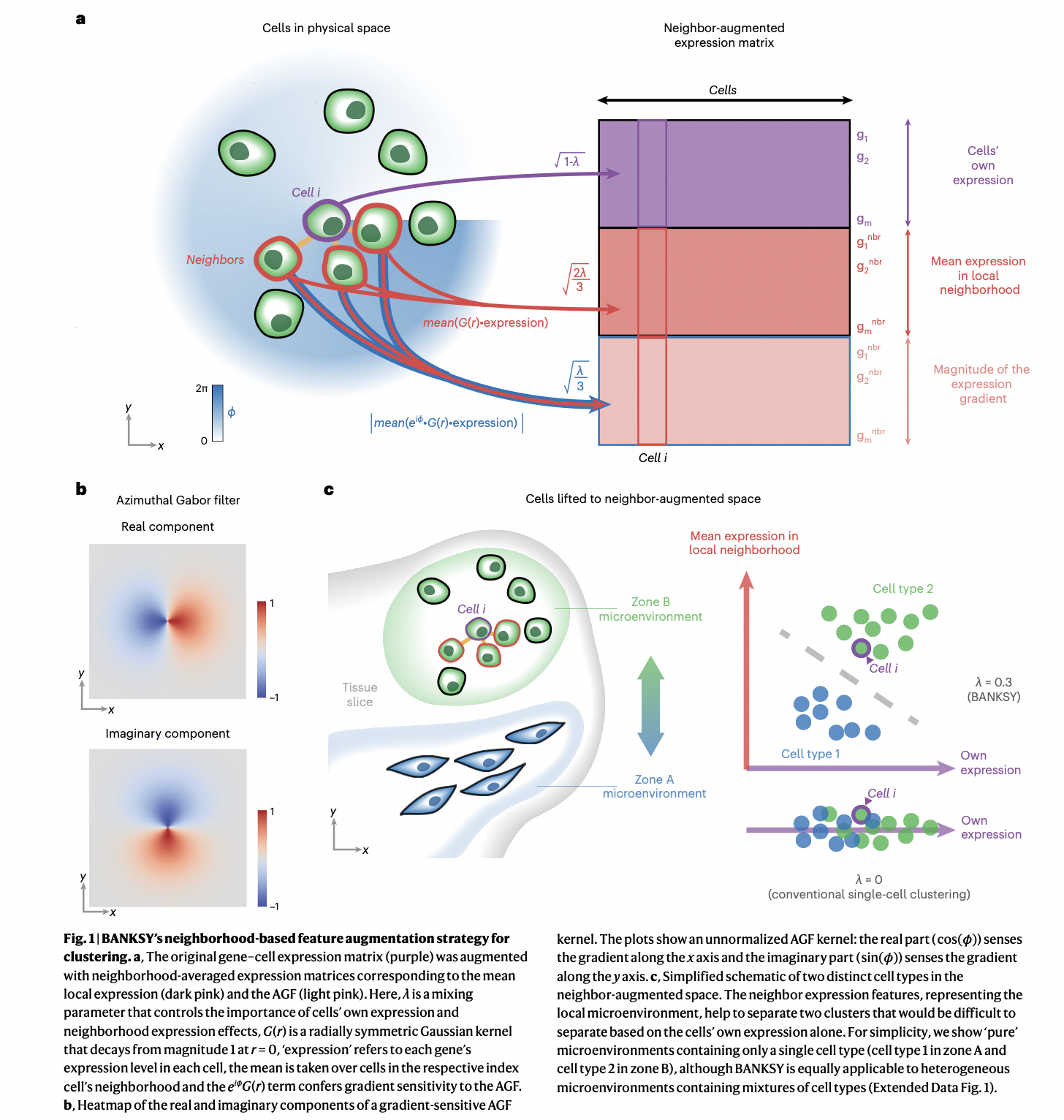
Recommended citation: Singhal, V., Chou, N., Lee, J. et al. (2024). "BANKSY unifies cell typing and tissue domain segmentation for scalable spatial omics data analysis." Nat Genet. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41588-024-01664-3